
Isostatic Graphite (CGI & ESM Series)
CGI and ESM series are isostatically pressed graphites which are produced by the method of Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP). This very fine grain graphite material allows high densities to be achieved.
Properties of isostatic graphite
- high strength
- excellent resistance to thermal shock
- high temperature and oxidation resistance
- low electrical resistance
- good corrosion resistance
- precise machining
- low content of impurities
Manufacturing process of isostatic graphite
Isostatic pressing is a multi-stage process and enables to obtain blocks with extremely homogeneous structure, which have constant physical parameters in each section and point.
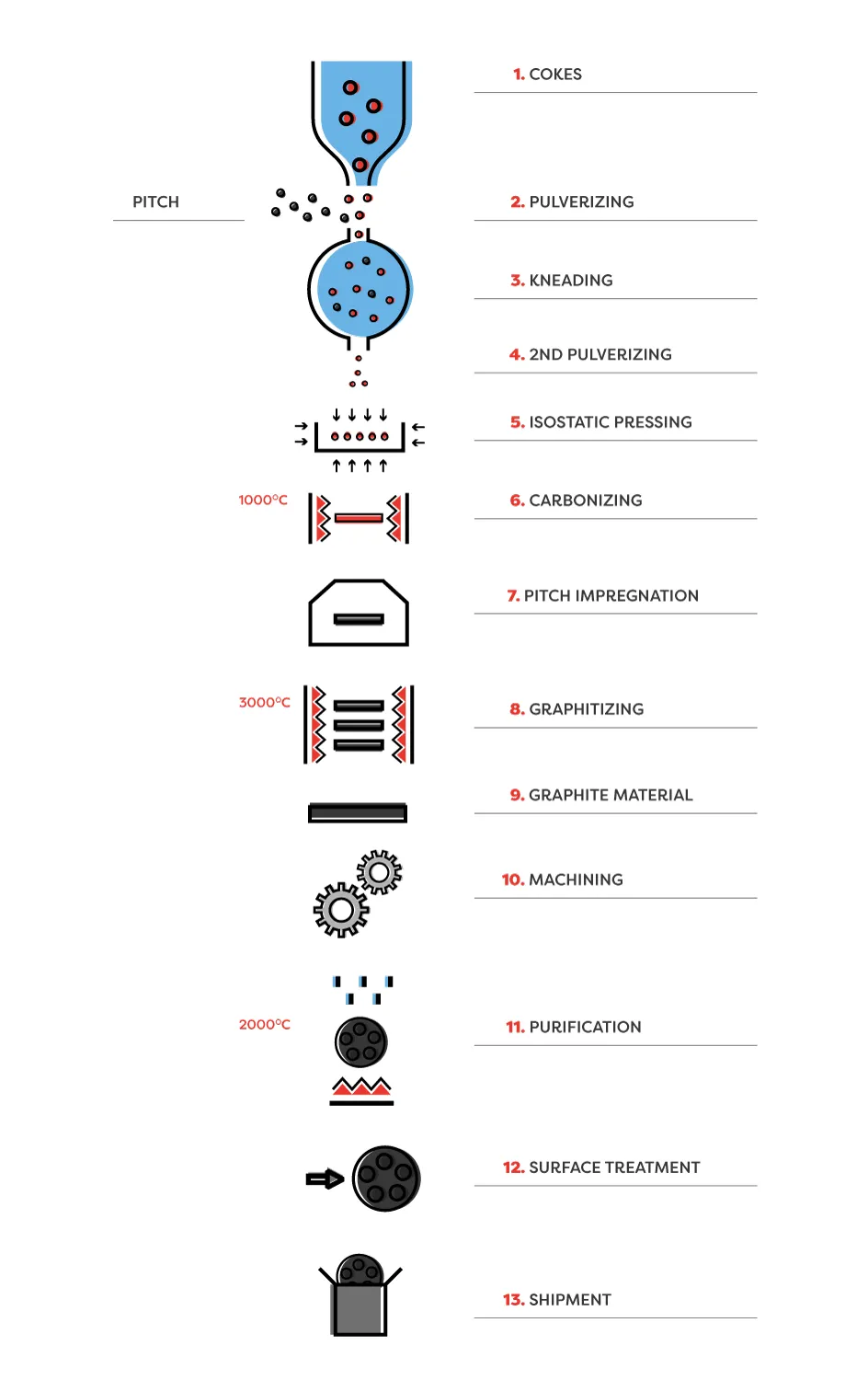
1. COKES
Coke is a component produced in oil refineries by heating hard coal (600-1200°C). This process takes place in a specially designed coke oven, using combustion gases and limited oxygen availability. It has a higher calorific value than conventional fossil coal.
2. PULVERIZING
After the raw materials have been checked, they are pulverised to a certain grain size. Special machines, which grind the material, transfer the obtained very fine coal dust into special bags and it is sorted according to the grain size.
PITCH
This is a by-product of coking (i.e. roasting without air at 1000-1200°C) of hard coal. Pitch is a dense black liquid.
3. KNEADING
When the coke milling process is completed, it is combined with pitch. Both raw materials are mixed at high temperatures so that the coal can melt and combine with the coke grains.
4. 2ND PULVERIZING
After the mixing process, small carbon balls are formed, which must be milled again into very fine grains.
5. ISOSTATIC PRESSING
Once the fine grains of the required size are ready, the pressing stage follows. The obtained powder is placed in large moulds, which have sizes corresponding to the final block sizes. The powdered carbon in the moulds is exposed to high pressure (over 150 MPa), which applies equal force and pressure to the grains, so that they are symmetrically arranged and consequently distributed evenly. This method allows to obtain the same parameters of graphite across the whole mold.
6. CARBONIZING
The next and at the same time the longest stage (2-3 months) is baking in the furnace. Evenly pressed material is placed in large furnaces where the temperature reaches 1000°C. To avoid any defects or cracks, the temperature in the furnace is constantly controlled. When baking is finished, the block achieves the desired hardness.
7. PITCH IMPREGNATION
At this stage of the process, the block can be impregnated with pitch and burned again to reduce its porosity. Impregnation is usually done using pitch with a lower viscosity than the pitch used as a binder. A low viscosity is required to fill the gaps more precisely.
8. GRAPHITIZING
At this stage, the matrix of carbon atoms is already arranged in an orderly manner, and the process of transition from carbon to graphite is called graphitizing. Graphitizing is the heating of the produced blocks to a temperature of about 3000°C. After graphitizing, the density, electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance are significantly improved and the machining efficiency is increased.
9. GRAPHITE MATERIAL
After graphitization, it is essential to inspect all graphite properties - including grain size, density, bending and compression strength.
10. MACHINING
Once the material is completely ready and inspected, it can be manufactured according to customer documentation.
11. PURIFICATION
If isostatic graphite is used in semiconductor, silicon monocrystalline and atomic energy industries, it requires high purity, so all impurities must be removed by chemical methods. A typical practice of removing impurities of graphite is to place the graphitized product in a halogen gas and heat it to about 2000°C.
12. SURFACE TREATMENT
Depending on the application of graphite, its surfaces can be milled and have smooth surfaces.
13. SHIPMENT
After final machining, the finished graphite detail is packed and sent to the customer.
Graphite plates
We can deliver our isostatic graphite in the forms of:
- Graphite blocks
- Graphite plates
- Graphite rounds
- Graphite tubes
- Graphite sections
- EDM graphite electrodes for EDM process
- Graphite casting dies
- Graphite tools and accessories
- Graphite parts acc. to the drawing
Our machined isotatic graphite products can also be purified to <5ppm on request.
For further information on available dimensions, isostatic graphite grades and prices, please feel free to contact us. Our engineers will be pleased to advise you on the right material and answer all of your questions.